http://science.howstuffworks.com/life/genetic/question92.htmWhen forming sperm cells, the father's body randomly chooses genes from the two halves of the father's chromosomes. This means that every sperm cell contains a random mix of the father's parents' genes. The same thing happens when forming eggs. Therefore, each child that a couple produces is a random mix of the four grandparents' genes.
http://www.life123.com/parenting/education/genetics/how-much-dna-half-siblings-share.shtml
https://www.23andme.com/gen101/origins/
http://genetics.thetech.org/ask/ask318
Mixing and Matching Chromosomes
Human DNA is packaged into 23 pairs of chromosomes for a total of 46. One set of 23 comes from mom and the other set of 23 from dad.
This also means that chromosomes come in pairs. So we have a pair of chromosome 1's, a pair of chromosome 2's, etc.
Parents pass one of each pair to their kids. But the chromosome passed on isn't really one of the ones already there. Instead, it is a mix of the pair of them.
Before our chromosomes are put into either the sperm or the egg, something called recombination happens. Basically, the two chromosomes in a pair swap DNA with each other. The end result is a unique chromosome.
Let me show you a diagram to help explain what happens. I'll start out with just one pair of chromosomes from one parent to show how it works. Here are a pair of mom's chromosomes:
http://blogs.discovermagazine.com/gnxp/2011/02/why-siblings-differ-differently/#.UgveyfX4LBg
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-Yg89GY61DE
Genetics 101 Part 3: Where do your genes come from?
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qCLmR9-YY7o
Meiosis: Where the Sex Starts - Crash Course Biology #13
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rB_8dTuh73c
Meiosis
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a5yzRRvROpE
What is meant by genetic difference?
A one paragraph summary of human genetics: The human genome consists of 2.85 billion units of DNA in all, packaged in large, individual molecules known as chromosomes. A person inherits one set of 23 chromosomes from each parent, so that each cell of the body holds a total of 46 chromosomes. Before the eggs or sperm are generated, the number of chromosomes must be halved, since when egg and sperm unite it will double. But before the halving process, the germline cells make each chromosome inherited from the individual's father line up with its counterpart chromosome inherited from the mother. Each pair of chromosomes then swaps corresponding chunks of DNA with its counterpart, so that a new pair emerges, each of which is now a medley of maternal and paternal genes. Each member of the new pair is tugged to opposite sides of the cell, which then divides to generate eggs or sperm. A special feature of this process concerns the 23rd pair of chromosomes, known as the X and Y sex chromosomes. Because the Y carries the male-determining gene, which must never be swapped into the X, the two chromosomes do not exchange genes, except at their very tips. Long ago, the Y chromosome was the same length as the X, but it has shed genes because, through the lack of diversity generated by the swapping process, many of its genes fell into disuse. Sperm carry either an X or a Y chromosome, whereas eggs always carry an X. Fertilization creates individuals with an X-Y pair (men) or an X-X pair (women). A consequence of this process is that people carry separately in their cells the set of chromosomes inherited from their mother and father; it is only when they come to generate their own eggs and sperm that the maternal and paternal genes are assorted into new, recombined chromosomes.
Before The Dawn: Recovering The Lost History Of Our Ancestors Wade, p. 53.
Briefly, what makes the chromosomes in the cell nucleus so difficult to use for tracing evolutionary histories is their habit of scrambling information at each generation. Until the germline cells are into their final division which produces the gametes (sperm or eggs), the chromosomes lead separate lives and don't have a great deal to do with one another. However, in that final cell division, the pairs of chromosomes which have been inherited from each parent sidle up to one another, like mating earthworms, and start to exchange bits of DNA. After this canoodling they pull apart and go off to different gametes. But now they are no longer the same chromosomes but DNA mosaics. They have undergone what is called recombination. This is the ultimate genetic reason for sex itself, the potential for creating through recombination new and better gene arrangements that can advance evolution.
The Seven Daughters Of Eve: The Science That Reveals Our Genetic Ancestry. Sykes, p.159.
The six billion building blocks of DNA in a human are all actually divided into shorter pieces, known as chromosomes. Chromosomes vary in length from 250 million nucleotides to around 50 million, and the Y is one of the shorter ones...
Why are we so interested in the Y chromosome and not another piece of DNA? After all, the Y chromosome is just a bit player among the other chromosomal giants, with a limited role and very few functional genes. It isn't even found in women, and they seem to get along just fine without it. Why focus on this runt of the genome?
The answer has to do with a shuffled deck. All of our chromosomes come in pairs. Everyone gets one of each pair from their mother and from their father. Although each chromosome derives entirely from from them, neither is identical to one of Mom or Dad's own chromosomes. That's because when a parent's chromosomes are passed on to his or her children, they reassemble themselves in a new, shuffled way. A little bit of chromosome A gets tagged onto a little bit of chromosome B, and vice versa along their entire length, through recombination. Why this occurs is still largely a mystery, but it almost certainly serves some evolutionary purpose or it wouldn't be so widespread in nature. Perhaps it allows the occasional bad mutation in the parent to be left out of the transmitted chromosome, or perhaps it allows new combinations of good mutations to be created. The net effect is that a child's chromosomes are entirely unique to him or her. This is a large part of the reason why no two children (apart from identical twins) - ever look exactly alike. They are carrying unique combinations of genetic variants generated through this shuffling process.
While all of this shuffling is a good thing evolutionarily speaking (to help keep the species healthy, for example), it makes the job of geneticists who want to trace ancestry very difficult. The clean lines of descent that we follow through time are quickly lost if any shuffling occurs. We do have very short regions of shuffled chromosomes (geneticists call them haplotype blocks) that are maintained over many generations before they are broken up, but they are very short and don't allow us to follow ancestral lines very far back in the past. What we ideally want to study is a large piece of DNA that doesn't recombine. This is precisely what makes the Y chromosome is so important.
Deep Ancestry: Inside The Genographic Project. Wells, p. 37-38.
HEY, IF ALL GOES WELL, MY GRANCHILDREN WILL BE 1/8th MEXICAN, 1/8th FILIPINO, AND 3/4ths (75%) POLYNESIAN (HOPEFULLY THAT 75% POLYNESIAN WILL COME IN THE FORM OF HAWAIIAN, BUT IF NOT HAWAIIAN, THEN MOSTLY SAMOAN OR TONGAN; AT LEAST 50% SAMOAN OR TONGAN) AND MY GREAT GRANDCHILDREN WILL BE 1/16th MEXICAN, 1/16th FILIPINO And 7/8ths (87.5%) POLYNESIAN (AGAIN, HOPEFULLY THAT 87.5% POLYNESIAN WILL COME IN THE FORM OF HAWAIIAN). IN OTHER WORDS, I'M GOING TO TRY TO BREED THE MEXICAN AND FILIPINO OUT OF MY LINEAGE AND BREED THE POLYNESIAN INTO IT. YEE.
 |
| SEE THE FACIAL AFFINITY BETWEEN GERY AND I (I'M KIDDING. WE'RE REALLY NOT MEXICAN.)? I HEARD A PILIPINA NURSE SAY "ARGH DEY ALL PRUM DA SAME PARROTS [PARENTS]?" IN OTHER WORDS, SHE WAS WONDERING IF MY FATHER SIRED ALL OF US WITH THE SAME WOMAN (OUR MOTHER) OR WHETHER WE WERE A COMBINED FAMILY LIKE THE BRADY BUNCH. WELL, LET ME ANSWER THAT QUESTION FOR YOU HERE, PILIPINA. MY PARENTS HAVE BEEN MARRIED GOING ON 55 YEARS AND THROUGHOUT THOSE NEARLY 55 YEARS THEY'VE REMAINED SEXUALLY FAITHFUL TO ONE ANOTHER (ESPECIALLY MY MOM). SO YES, ALL OF MY SIBLINGS AND I ARE A PRODUCT OF THE SAME TWO PEOPLE, OUR BIOLOGICAL PARENTS, RICHARD (DICK) AND DOLORES DAGAMPAT. |
"He Looks Mexican!" I Only Look Mexican To People That Have No Experience With People Of Other Races Or Racially Admixed People. Why Is That I'm Able To Discern Other People's Race Or The Racial Makeup Of Racially Mixed People? Because I Have A Lot Of Experience With People Of Other Races, So I Can Tell The Differences In Facial Structure And Facial Features Among People Of Different Races. You Can't Because All You Know Are White, Black, And Mexican (Hispanic) Facial Features.
http://www.unz.com/gnxp/siblings-are-identical-twins-full-siblings-unrelated/?utm_source=rss&utm_medium=rss&utm_campaign=siblings-are-identical-twins-full-siblings-unrelated&utm_source=twitterfeed&utm_medium=twitter
Gery And I Don't Look Mexican. Well, We Look Mexican To People That Can't Accurately Discern The Racial Makeup Of Other People And Who Have Limited Experience With People Of Different Races (Races Different Than Their Own), But To People Who Have Experience With People Of Others Races And Who Can Accurately Determine One's Racial Makeup WE DON'T REALLY LOOK MEXICAN. For Instance, If We Were Living In Hawaii Most Locals (Non-Hawaiian Locals And Racially Mixed Native Hawaiians) Wouldn't Look At Us And Think That We Were JUST MEXICAN. They'd Be Able To Tell That We Were Mixed With Some Polynesian.
http://scienceblogs.com/gnxp/2007/11/26/mixedrace-but-homogeneous-appe/
Hey, Filipino Mothers With A White Husband Or White Boyfriend Who Have Given Birth To A White/Filipino Child, Don't Look At My Sisters Children And Think That They're Like Your Kids Because They Aren't. Genetically They Aren't And Socially And Culturally They Aren't. WE ARE NOT FILIPINO LIKE YOU.
IF
YOU WERE TO SEE MY SISTER TINA AND MY BROTHER GERY WALKING DOWN THE
STREET TOGETHER YOU WOULDN'T THINK THEY WERE RELATED. YOU'D THINK THAT
THEY WERE FROM DIFFERENT FAMILIES AND DIFFERENT RACES (FILIPINO AND
MEXICAN, RESPECTIVELY). BUT, AS YOU KNOW BY NOW, YOU'D BE WRONG TO MAKE
SUCH AN ASSUMPTION. WHY WOULD YOU BE WRONG? BECAUSE THEY'RE SIBLINGS AND
AS SUCH THEY SHARE 50% OF THE SAME GENES THAT THEY INHERITED FROM THEIR
PARENTS. WHY DO THEY LOOK SO DIFFERENT EVEN THOUGH THEY'RE SIBLINGS WHO
SHARE 50% OF THE SAME DNA AND WERE CREATED BY THE SAME PARENTS? BECAUSE
OF GENETIC RECOMBINATION, WHICH WAS INTENSIFIED BY THE FACT THAT
THEY'RE GENETIC ADMIXTURES CREATED BY DIFFERENT GENES (ALLELES) FROM
DIFFERENT RACES. (GENETIC RECOMBINATION CREATED NEW CHROMOSOMES FOR EACH
INDIVIDUAL SIBLING AND ON THOSE NEW CHROMOSOME'S ARE SOME OF THE
FATHER'S GENES (FILIPINO OR HAWAIIAN IN OUR CASE) AND SOME OF THE
MOTHER'S GENES (MEXICAN AND EUROPEAN* (ALEMAN) IN OUR CASE) ARRANGED IN A
WAY THAT'S DIFFERENT FROM EITHER PARENT AND UNIQUE TO THE OFFSPRING
THAT INHERITED THIS COMBINATION.)
*IMMA WOOD


WHEN I TRANSFERRED FROM WILSON HIGH SCHOOL TO LOS ALTOS HIGH SCHOOL MY SISTER FOLLOWED ME THE FOLLOWING SEMESTER. ONE OF THE ASIAN ACQUAINTANCES I MADE AT LOS ALTOS FOUND OUT THAT MY SISTER HAD TRANSFERRED AND WAS CURIOUS AS TO WHAT SHE LOOKED LIKE. SO I TOLD HIM WHERE TO FIND HER. WHEN HE SAW HER AND GOT BACK TO ME ABOUT IT HE WAS ALMOST IN A STATE OF SHOCK. HE COULDN'T BELIEVE HOW DIFFERENTLY SHE LOOKED FROM ME. HIS WORDS WERE SOMETHING ALONG THE LINES OF "I THOUGHT SHE WAS GOING TO BE SMALL AND SCRAWNY. SHE'S THE EXACT OPPOSITE. SHE HARDLY LOOKS LIKE YOU." I BELIEVE HE WAS EXPECTING A FEMALE VERSION OF ME RELATIVE TO MY SIZE. SO HE MUST HAVE BEEN ANTICIPATING HER TO BE THIN (NOT BIG BODIED), SHORT, AND OVERALL PETITE, BUT HE WAS MISTAKEN. AGAIN, THIS IS A RESULT OF GENETIC RECOMBINATION ENHANCED BY THE FACT THAT WE'RE RACIAL ADMIXTURES. KATY INHERITED CHROMOSOMES WITH GENES FROM EACH OF THE RACES THAT WE CONSIST OF AND THOSE GENES THAT CODE FOR BODY TYPE, FACIAL TYPE, HAIR TYPE, ETC. DIFFERED FROM MINE. IN OTHER WORDS, HER DOMINANT* BODY TYPE GENES MAY BE POLYNESIAN (HAWAIIAN) WHEREAS MINE MAY BE FILIPINO (MORE ECTOMORPHIC), HER DOMINANT FACIAL TYPE GENES MAY BE HAWAIIAN OR FILIPINO WHILE MINE MAY BE MEXICAN, HER DOMINANT HAIR TYPE GENES MAY BE FILIPINO WHILE MINE MAY BE HAWAIIAN OR MEXICAN, ETC., ETC., ETC. DO YOU UNDERSTAND?
*FORGIVE ME, THE EXPRESSION OF TRAITS IS NOT ALWAYS DEPENDENT ON DOMINANT GENES. SOME TRAITS ARE A COMBINATION OF BOTH DOMINANT AND RECESSIVE GENES (THEY BOTH INTERACT TO PRODUCE THE PHYSICAL OR MENTAL CHARACTERISTIC), SO THEIR EXPRESSION IS A RESULT OF CODOMINANCE OR SEMIDOMINANCE.
KATY PRIMARILY ASSOCIATED WITH FILIPINOS AND SOME EAST ASIANS (CHINESE, KOREANS, JAPANESE) IN HIGH SCHOOL, BUT HER BEST FRIEND IN HIGH SCHOOL (WHO REMAINS TO BE HER BEST FRIEND) WAS ITALIAN AND MEXICAN.
 | ||||||||||||||
RICHIE WAS
SOMEWHERE WITH ONE OF HIS WHITE FRIENDS IN THE 80s AND HIS FRIEND TURNED
TO HIM AND SAID "HEY, DID YOU SEE THAT ORIENTAL GIRL? SHE'S BEAUTIFUL"
OR SOMETHING ALONG THOSE LINES. SO RICHIE ASKED HIM TO POINT HER OUT.
WHEN RICHIE REALIZED WHO HIS FRIEND WAS TALKING ABOUT HE LAUGHED AND
TOLD HIM "THAT'S MY SISTER AND WE'RE NOT ORIENTAL." RICHIE'S FRIEND
COULDN'T BELIEVE THAT THEY WERE RELATED, LET ALONE BROTHER AND SISTER.
(RICHIE HAS MORE OF A POLYNESIAN LOOK WHEREAS TINA HAS MORE OF A
FILIPINO LOOK. WHAT IS THIS A RESULT OF? GENETIC RECOMBINATION ENHANCED
BY THE FACT THAT THEY'RE GENETIC ADMIXTURES WITH GENES FROM DIFFERENT
RACES.)
|
 |
| Fred's Ex-Wife Was Half White And Half Chinese. She Went To UCSB. She's Now A Math Teacher, I Believe. Look At His Son, Nick: https://twitter.com/ncarneysb See The Facial Affinities Between Nick And Fred Jr.? |
 |
| Fred Jr. With His Daughter. Our Cousin Fred Is Genetically Very Similar To My Siblings And I (More So Than Most Cousins Are To One Another). Why? Because His Mom Comes From The Same Genetic Stock As Our Mom And His Dad Comes From The Same Genetic Stock As Our Dad. Socially, However, Fred Jr. Is Not As Similar To Us. Why? Because He Wasn't Raised By A Father And Mother Like Ours, Didn't Grow Up In A Household Like Ours, Didn't Live In The Places We Lived, And Didn't Associate With The Type Of People We Associated With. So Although There Are Some Similarities Between He And My Siblings They're Mostly A Result Of He Sharing Some Of The Same Genes As Them. (The Only Sibling Of Ours That's Somewhat Close To Him Is David. None Of My Other Siblings Were Especially Close To Him.) http://www.psychologytoday.com/blog/the-scientific-fundamentalist/201103/criminals-look-different-noncriminals Pimp I'm A Criminal! |
 |
| PRACTICE LOOKING HARD (I PUT ON A DIFFERENT FACE EVERY TIME I TAKE A PHOTO. WHY? BECAUSE I'M AN ACTOR. I'M NOT ACTIVE I'M AN ACTOR.) http://www.thememagazine.com/stories/the-genetics-of-sibling-rivalry/ The theory is essentially this: parents and children, above all else, want to make sure their genes get passed safely to the next generation—but the way in which a child and a parent ensure that safe passage differs. From the parents’ perspective, it is best to lavish attention equally among their offspring. Equal investment in their children’s survival increases the chances that all offspring will successfully pass their genes onward, to their grandchildren. Children, on the other hand, see things differently. Each child is made up of genes from their parents, fifty percent from their mother and fifty percent from their father—which, technically speaking, add up to one-hundred percent of their own genes. A child is thus twice as related to herself as she is to her sibling. For instance, Alexa contains one-hundred percent of her own genes, but she also shares fifty percent of her genes with her sister, Kaili. So Alexa has twice as many “Alexa genes” as does Kaili and should therefore, by the logic of maximizing one’s genetic propagation, get twice as much parental attention. From Alexa’s perspective, it is perfectly fair that she receive two-thirds of parental attention, and that Kaili receive the remaining one-third. (Alexa doesn’t give a damn about the other fifty percent of “Kaili genes.”) Of course, it’s the mirror image from Kaili’s perspective. The seeds of rivalry are thus deeply planted. http://chronicle.com/article/Parent-Child-Conflict-Its-in/130387/?sid=at&utm_source=at&utm_medium=en http://www.psychologytoday.com/blog/the-imprinted-brain/201207/parent-offspring-conflict-time-listen-the-argument |
 |
| Them Dawgs Look Good (Tasty Looking)! |
*Just About All Of My Brother's Girlfriends Have Been WHITE, Except For Gery's Girlfriend's. For Instance, Prior To Steven Marrying Amparo, All Of His Girlfriends Were WHITE, Except For A Japanese Girl, Just Like The Majority Of My Other Brothers' Girlfriend's Were WHITE (Your Peer Group, The People You Surround Yourself With Has The Greatest Influence On Your Choice Of Mate). (All Of My Sister's Boyfriends Have Been WHITE.)
| ||||
 |
| Here's The Japanese Girl. Her Name Is Kenny. Kenny Was Steven's Girlfriend In High School And A Little After High School. Notice The High, Broad Cheekbones, Broad Chin, And Brachycephalic Head? She Was Fairly Attractive (Japanese As A Whole Have A Higher Level Attractiveness Than Other East Asian Groups). See My Fat Baby Legs Behind Her? http://asianeyes.wordpress.com/beauty/ Can You You Tell The Difference Among Japanese, Koreans, And Chinese Based On Facial Features? I Can. In Fact, I've Gotten So Good That I Can Differentiate Between Taiwanese And Chinese Both Of Whom Are Genetically Very Similar And Share Strong Facial Affinities (They Closely Resemble One Another). I'm Not So Good With Southeast Asians (Vietnamese, Thais, Cambodians, Burmese, Etc.) Because They're Lower Socioeconomic Status Groups That I Didn't Grow Up Around. But I Can Distinguish Them (Southeast Asians) From East Asians. |
http://psychothalamus.blogspot.com/2010/10/racial-differences-in-concept-of-beauty.html
I Can Pinpoint The Ethnic Group That An East Asian Comes From Just by Looking At He/She. I Can Do The Same With Southeast Asians, But I'm Typically Not As Accurate. Can You? I Don't Think So.
 |
| Can You Read This? (LOCK HIS NIGGER ASS UP.) |
Neil Risch, an eminent geneticist now at the University of California, San Francisco, was the first to say in print that the emerging view of human population structure had major points of correspondence with the public conception of race. Risch's article was sparked by his irritation at the sociologists' race-is-not-biological dogma surfacing in, of all places, the New England Journal of Medicine, a leading journal of medical research. "Race is a social construct, not a scientific classification," declared an editorial by Robert S. Schwartz, the journal's deputy editor. Since race is "biological meaningless," Schwartz argued, it should not play any part in a physician's work. A similar editorial, though less absolutist, appear in the journal Nature Genetics.
Much of this discussion, Risch wrote in rebuttal of the two editorials, "does not derive from an objective scientific perspective."...Numerous genetic studies of the human population have found that differences are greatest between continents. These studies, he said, "have recapitulated the classical definition of races based on continental ancestry." Updating those definitions, Risch and his colleagues suggested that racial groups should be defined on the basis of continent origin, with ethnicity being used to describe smaller subdivisions within races.
The five continent-based races, Risch's view, are as follows:
Africans are those whose primary ancestry is in sub-Saharan Africa. This includes African Americans and Afro-Caribbeans.
Caucasians are people of western Eurasia - Europeans, Middle Easterners, North Africans and those of the Indian subcontinent (India and Pakistan).
Asians are people of eastern Eurasia (China, Japan, Indochina, the Philippines and Siberia).
Pacific Islanders are Australian aborigines and people of New Guinea, Melanesia and Micronesia.
Native Americans are the original inhabitants of North and South America.
Within each continental race there are gradients of skin color, from the light-skinned Khoisan speakers of Southern Africa to the darker-skinned Bantu speakers of western and central Africa, from the lighter-skinned Scandinavians to the darker-skinned peoples of southern India. Skin color is therefore an ambiguous indicator of continental race.
At the boundaries of these continental divisions are several groups formed by intermarriage between the two neighboring races, a condition for which geneticists use the term "admixture." Ethiopians and Somalians, for instance, are an admixture of Caucasians and Africans. "The existence of such intermediate groups should not, however, overshadow the fact that the greatest genetic structure that exists in the human population occurs at the racial level," Risch says.
In the United States there are several populations formed by intermarriage between members of two racial groups. African Americans, largely as a result of slavery, have a share of Caucasian genes that ranges from 12% to 23% in various populations, with an average of about 17%. "Despite the admixture, African Americans remain a largely African group, reflecting primarily their African origins from a genetic perspective," Risch says.
Another group of admixed populations is counted by the U.S. Census Bureau as Hispanic although Hispanic is a linguistic, not a racial, category. Hispanics vary in their admixture in different parts of the country. In the southwestern United States, Hispanics are mostly Mexican Americans, whose ancestry is 39% Native American, 58% Caucasian, and 3% African, according to one recent estimate. East coast Hispanics come mostly from the Caribbean and have a larger proportion of African genes.
The United States is often referred to as a melting pot of races but the rate of mixing is slower than might be assumed. Figures from the 2000 U.S. census indicate that U.S. citizens do not marry each other at random. Racial endogamy (marrying within the racial group) is the rule: 97.6% of respondents reported themselves to be of one race; only 2.4% said they were of more than one race, presumably having parents of different races. Some 75% of Americans declared themselves to be white, that is, Caucasian; 12.3% said they were black or African American; 3.6% were Asian, 1% Native American, and 5.5% of other races.
These continental groups reflect the leading roles of geography and endogamy in shaping human races. As long as everyone intermarries, as would doubtless have been the case in the ancestral human population, there is a single genetic pool. New diversity - that is, new altenative versions of genes - accumulates through mutations, and old diversity is eliminated by drift, but these changes occur within a common pool. Any substantial bar to intermarriage, however, whether a mountain range or a religious ban on marrying outsiders, will set up two genetic pools. Since mutation and drift are both random processes, the changes in the two pools will now take place independently. From that point on, the two populations may follow different evolutionary paths. Migration between the two will sharply reduce genetic difference; time and distance will increase it.
The starting point for the emergence of human races would have been the dispersal, within Africa, from the ancestral homeland some 50,000 years ago. Before people left for the world beyond, the human population in Africa had apparently fragmented, doubtless by geographical distance, into several different populations. As already noted, those who left Africa belonged to just one of those populations, those descended from the L3 branch of the mitochondrial DNA tree. They carried away in their genes only a subset of the African genetic diversity, meaning only some of the alleles of each gene. That fact alone set them on a potentially different evolutionary path.
The emigrants eventually spread out over the rest of the globe and themselves fragmented into many even smaller populations. The smaller a population, the greater is the force of genetic drift, which reduces the number of available alleles. Without interbreeding to keep the human gene pool mixed, the populations of each continent or region would over time have become more distant and less like the others.
The importance of drift in differentiating a static population has recently been recognized in the population of Iceland. As mentioned earlier, even though the island has been settled for only 1,000 years, the people in each region have become sufficiently different genetically that by sampling Icelanders' genome in just 40 different places it is possible to tell which of 11 regions of the island they come from. In the rest of the world, with some 50 times longer for genetic forces to act, and many severe impediments to movement, a much greater degree of differentiation would be expected.
Besides drift, another differentiating force on the world's separate human populations would have been natural selection. Selection may have pressed particularly hard on the people who left the African homeland, since they would have had to adapt to a radically new diet, terrain and climates. A particularly striking example of selection is a recently discovered gene variant that causes pale skin in Caucasians. Almost all African and Asians have the same, ancient form of the gene, which is known at present as SLC24A5. Some 99% or more of Europeans have a new version, that must have arisen after Caucasians and East Asians had become separate populations. The new version presumably became almost universal among Caucasians because the pale skin it conferred was of overwhelming advantage, whether for reasons of health or sexual attractiveness or both. A different gene, yet to discovered, must give East Asians their pale skin.
As Darwin suggested, sexual selection, the partly capricious taste of women and men for partners of a certain type, as well as competition between men, may have been a strong selective force, and one that acted somewhat independently in each human population. Disease has certainly influenced the human genome as people in different regions respond to local diseases like malaria. Warfare, an unremitting pressure, surely played a major role in shaping populations. And another powerful molder of human populations would have been climate, especially the adaptations necessary for living in northern latitudes and the violent climatic swings of the late Pleistocene.
Given all these evolutionary forces at work, it is not surprising that the widely dispersed human populations in various continents acquired their own distinctive variations on the general human theme. This genetic-geographical difference is reflected in the familiar trees drawn on the basis of mitochondrial DNA or the Y chromosome, and on several other kinds of genetic elements. Risch cited some of these studies as proof of the division of the human population into continent based races.
A few months after Risch's article of 2002,a more comprehensive study by Marcus Feldman of Standfor University reached a very similar conclusion. Instead of examining just a few markers, or sites on the DNA,as many previous studies have done, Feldman and his colleagues looked at 377 sites throughout the genome, a larger and more representative sample. This was done for each of 1,000 people from 52 populations around the world. A computer was then instructed to group the individuals, based on their DNA differences at the 377 sites, into clusters. They fell naturally into 5 clusters, corresponding to their five continents of origin - Africa, western Eurasia (Europe, the Middle East, the Indian subcontinent), East Africa, Oceania and the Americas.
Feldman and his colleagues did not use the word "race" in their article, referring instead to "structure" and "self-reported population ancestry" (meaning a person's own identification of their race)., but he acknowledged in an interview that the finding essentially confirmed the popular conception of race."Neil's article was theoretical and this is the data that backs up what he said," Feldman commented in reference to Risch's study.
A consequence of the Risch and Feldman studies is that they provide, for the first time, an objective way of ascertaining an individual’s race. Most previous systems of race classification, with the principal exception of modern craniometry, have been based on characteristics like skin color, which vary in an unsystematic way, and were often designed with a malign agenda such as demonstrating one race’s alleged superiority to others. Not only does the genetic definition of race have no such agenda, but it has nothing directly to do with any physical attribute.
The reason is that the genetic markers used to identify race are not part of the genes or their control regions, so far as is known, and therefore play no part in the physical appearance or behavior of an individual. Presumably they are indirectly correlated with genes that do control the body’s physical makeup, but the connection is indirect and at present unknown.
The DNA markers analyzed by the Feldman team are of the same type as is used in the DNA fingerprinting of forensic cases. At various sites on the human genome the sequence of DNA units goes into a sort of stutter, known as a short tandem repeat because a few units of DNA are repeated several times over, as in AC-AC-AC-AC-AC. For some reason, these stutters tend to confuse the cell’s DNA copying apparatus, which every dozen or so generations may accidentally either add or delete a repeat. The exact number of repeats at a given site is therefore quite variable from one person to another, and so can be made the basis of systems for identifying populations or individuals.
Only some 3% of the DNA in the genome is devoted to genes; the rest of the DNA is mostly yards of filler material. The short tandem repeats are part of the filler material so do not affect a person’s physical makeup. But some repeats lie close to genes, some of which have evolved in different ways in the various races. By selecting the right repeats, geneticists can find ones that are quite diagnostic of race, even though at present they have little idea which genes it is that give people of different races their different appearance.
Risch calculated that if the sites with short tandem repeats were chosen entirely at random, analysis of about 100 sites should suffice to say which of the five major races a person comes from. But as few as 30 sites would be enough if the sites were specially chosen so as to be diagnostic of race. Many hundreds of markers would be needed to distinguish, within a race, between two populations or ethnicities, Risch estimated.
Sets of these sites, known as Ancestry Informative Markers, can be used to identify not just an individual’s race but the racial origin of individual sections of a person’s genome. A company called DNAPrint Genomics has already started offering a test to assess people’s continent of origin and, if of mixed race, the proportions of ancestry due to different races. The test is based on a set of markers identified by Mark Shriver, a geneticist at Pennsylvania State University. It has already proved useful in police inquiries by identifying the race of a suspected serial killer from tissue collected at a crime scene. In June 2003 police believed that a serial killer in Louisiana was white, but were informed otherwise by DNAPrint Genomics, whose test showed the killer’s ancestry was 85% African and 15% American Indian; they then arrested a suspect who was black. The reliability of the test has not yet been established, but if it helps police identify a suspect, the suspect’s DNA can then be compared with the crime scene DNA in the usual way.
Feldman and his colleagues say they needed varying numbers of markers—in this case sites with tandem repeats—to identify a person’s continent of origin, depending on the genetic variability of the race in question. Native Americans could be assigned to their continent of origin with just 100 markers, whereas almost all 377 markers were required to identify Middle Easterners. This is because Native Americans are all descended from their Siberian founders whereas Middle Easterners are a more complex genetic blend; they are mostly Caucasian but some, like the Bedouin, have an African contribution.
Feldman’s method gives a glimpse of how deeply genetic markers may be able to reach into population history. The computer program used to sort the genome samples into continental clusters could also split an individual’s genome into different parts if the person was of mixed ancestry. People from the Hazara and Uighur of Central Asia, long a crossroads between east and west, emerged with genomes roughly half Caucasian and half East Asian in origin. The Surui, a fairly isolated people of Brazil, have genomes that are
entirely American (in terms of the computer program’s 5 racial clusters), whereas Mayan genomes are American with a strong dash of European and East Asian admixture.
With extra markers, and ones chosen to be more diagnostic of geographical origins, it should be possible to explore a population’s ancestry and history in a much more detailed way. For geneticists, the essence of race is not politics but history: race defines through which branch of the human family tree people trace their descent.
Before The Dawn: Recovering The Lost History Of Our Ancestors Wade, p. 183-190.
http://permaculteur.free.fr/ecoanarchisme/Before%20the%20Dawn.pdf
http://www.amazon.com/Eden-East-Drowned-Continent-Southeast/dp/0753806797/ref=sr_1_2?s=books&ie=UTF8&qid=1376693800&sr=1-2
Island-hopping study shows the most likely route the first people took to Australia http://theconversation.com/island-hopping-study-shows-the-most-likely-route-the-first-people-took-to-australia-93120?utm_source=twitter&utm_medium=twitterbutton … via @ConversationEDU
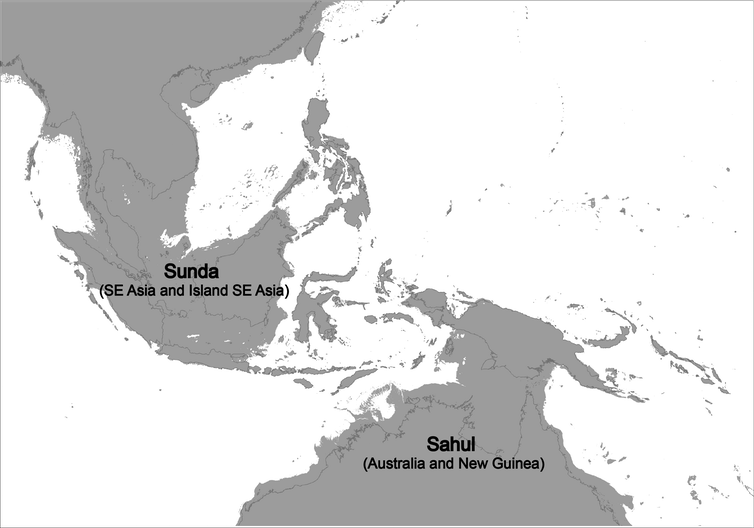
MME-Sunda Shelf Archaeology Project- "Genetic Theories of Dr. Oppenheimer
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dPaWdK8gt7c
Geneticist clarifies role of Proto-Malays in human origin

http://www.internetlooks.com/humandifferentiation.html
http://web.mesacc.edu/dept/d10/asb/origins/race/racial_odyssey.html
http://webspace.ship.edu/cgboer/race.html
http://www.amren.com/news/2008/02/race_and_physic_1/
http://whyevolutionistrue.wordpress.com/2012/02/28/are-there-human-races/
 |
| http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8183HPmA2_I&feature=relmfu Human Prehistory 101 (Part 1 of 3): Out of (Eastern) Africa (WATCH ALL 3 PARTS OF THIS SERIES) |


.jpg)














.jpg)
.jpg)